目录
一、HashMap的底层实现
HashMap 是 Java 中常用的数据结构之一,用于存储键值对。它的底层实现是基于哈希表(Hash Table)。以下是 HashMap 的底层实现细节:
-
数组:
HashMap内部维护一个数组,数组的每个元素称为桶(bucket)。数组的长度通常是2的幂,这是为了便于哈希函数计算索引值。 -
链表和红黑树: 在每个桶中,如果发生哈希冲突(即两个不同的键具有相同的哈希值),那么这些键值对会以链表的形式存储在同一个桶中。从Java 8 开始,当链表的长度超过一定阈值时,会将链表转换为红黑树,以提高查询性能。
-
哈希函数:
HashMap使用键的哈希码来计算索引值。哈希码是通过调用键的hashCode()方法得到的。计算索引值的过程涉及到取模运算,即index = hashCode % arrayLength。 -
扩容: 当
HashMap中的元素个数超过了容量与负载因子的乘积时,就会触发扩容操作。负载因子是一个表示填充程度的浮点数,默认为0.75。扩容时,数组的长度会变为原来的两倍,并且原来的键值对需要重新计算哈希码和索引值,然后放入新的数组中。 -
并发性:
HashMap在多线程环境下是不安全的,因为多个线程可能同时修改HashMap,导致数据不一致。在Java 8及之后的版本中,提供了ConcurrentHashMap来解决这个问题,它通过分段锁和 CAS 操作来保证并发安全性。
参考资料
二、HashMap扩容机制
概念
HashMap 的扩容是为了保持其在负载因子(load factor)范围内的性能。负载因子是一个表示填充程度的浮点数,默认值为 0.75。当 HashMap 中的元素数量达到容量与负载因子的乘积时,就会触发扩容操作。
详细扩容:
1、初始容量
当创建一个新的 HashMap 时,它会有一个初始容量,通常是16。这个初始容量可以在构造函数中指定,但如果不指定,默认值为16。
2、添加元素
当往 HashMap 中添加键值对时,首先计算键的哈希码,并根据哈希码计算索引值。如果该索引位置没有元素,直接插入;如果有元素,发生哈希冲突,就会以链表的形式添加到相应的桶中。
3、元素数量检查
在每次添加元素后,HashMap 会检查当前元素的数量是否超过了容量与负载因子的乘积,即 size > threshold = capacity * loadFactor。
4、触发扩容
如果元素数量超过了阈值,就会触发扩容操作。扩容时,HashMap 将会创建一个新的数组,长度是原数组的两倍(newCapacity = oldCapacity * 2),然后将原数组中的元素重新计算哈希码和索引值,放入新数组中。
5、迁移元素
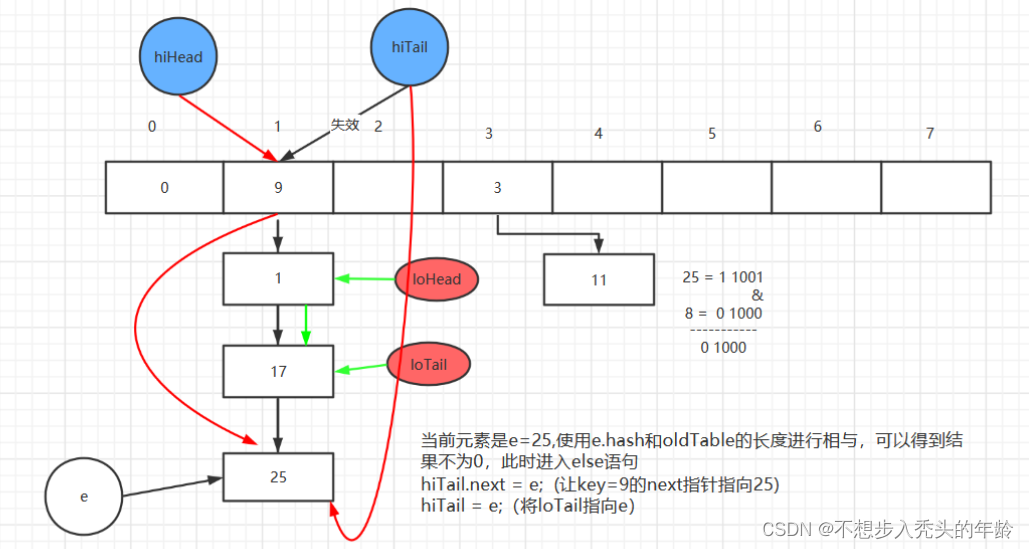
扩容后,原数组中的每个桶可能包含一个链表或一棵红黑树。HashMap 将遍历原数组中的每个桶,然后将其中的元素迁移到新数组中。在迁移的过程中,由于新数组长度是原数组长度的两倍,因此每个元素的索引值可能会发生变化。
6、更新容量和阈值
扩容后,HashMap 更新自己的容量和阈值。容量变为新数组的长度,阈值变为新容量与负载因子的乘积。
代码:
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import java.util.LinkedList;
-
- public class MyHashMap<K, V> {
- private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
- private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
-
- private Node<K, V>[] table;
- private int size;
- private int threshold;
-
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public MyHashMap() {
- table = new Node[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
- threshold = (int) (DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
- }
-
- public void put(K key, V value) {
- if (key == null) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Key cannot be null");
- }
-
- if (size + 1 > threshold) {
- resize();
- }
-
- int hash = hash(key);
- int index = getIndex(hash, table.length);
-
- if (table[index] == null) {
- table[index] = new Node<>(hash, key, value);
- size++;
- } else {
- LinkedList<Node<K, V>> bucket = table[index].getBucket();
- for (Node<K, V> node : bucket) {
- if (node.key.equals(key)) {
- // Key already exists, update the value
- node.value = value;
- return;
- }
- }
- // Key does not exist in the bucket, add a new node
- bucket.add(new Node<>(hash, key, value));
- size++;
- }
- }
-
- private void resize() {
- int oldCapacity = table.length;
- int newCapacity = oldCapacity * 2;
- threshold = (int) (newCapacity * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
-
- Node<K, V>[] newTable = new Node[newCapacity];
- for (Node<K, V> node : table) {
- if (node != null) {
- LinkedList<Node<K, V>> bucket = node.getBucket();
- for (Node<K, V> entry : bucket) {
- int hash = hash(entry.key);
- int index = getIndex(hash, newCapacity);
-
- if (newTable[index] == null) {
- newTable[index] = new Node<>(hash, entry.key, entry.value);
- } else {
- newTable[index].getBucket().add(new Node<>(hash, entry.key, entry.value));
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- table = newTable;
- }
-
- private int hash(K key) {
- // Simplified hash function for illustration purposes
- return key.hashCode();
- }
-
- private int getIndex(int hash, int length) {
- // Simplified index calculation for illustration purposes
- return hash % length;
- }
-
- private static class Node<K, V> {
- private final int hash;
- private final K key;
- private V value;
-
- private LinkedList<Node<K, V>> bucket;
- public Node(int hash, K key, V value) {
- this.hash = hash;
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- this.bucket = new LinkedList<>();
- this.bucket.add(this);
- }
-
- public LinkedList<Node<K, V>> getBucket() {
- return bucket;
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- MyHashMap<String, Integer> myHashMap = new MyHashMap<>();
- myHashMap.put("One", 1);
- myHashMap.put("Two", 2);
- myHashMap.put("Three", 3);
-
- // ... (additional testing and usage)
- }
- }


评论记录:
回复评论: