
一、C语言的输入与输出
C语言中我们用到的最频繁的输入输出方式就是scanf ()与printf()。 scanf(): 从标准输入设备(键盘)读取数据,并将值存放在变量中。printf(): 将指定的文字/字符串输出到标准输出设备(屏幕)。注意宽度输出和精度输出控制。C语言借助了相应的缓冲区来进行输入与输出。如下图所示:
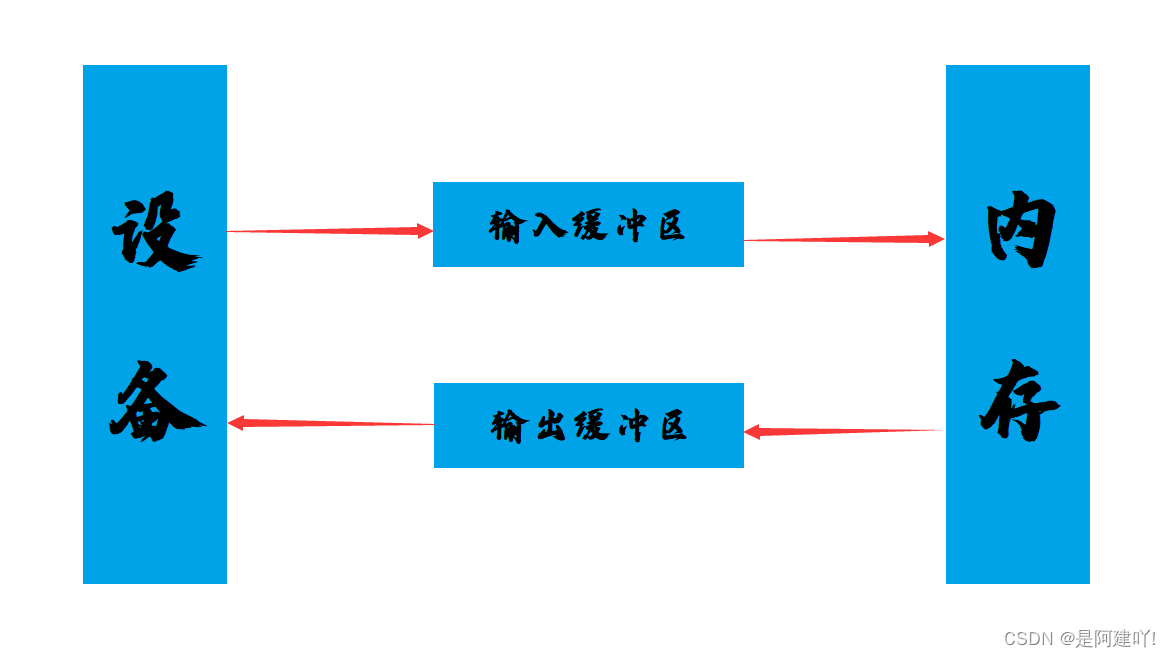
对输入输出缓冲区的理解:
1.可以屏蔽掉低级I/O的实现,低级I/O的实现依赖操作系统本身内核的实现,所以如果能够屏蔽这部分的差异,可以很容易写出可移植的程序。
2.可以使用这部分的内容实现“行”读取的行为,对于计算机而言是没有“行”这个概念,有了这部分,就可以定义“行”的概念,然后解析缓冲区的内容,返回一个“行”。
二、流是什么
“流”即是流动的意思,是物质从一处向另一处流动的过程,是对一种有序连续且具有方向性的数据( 其单位可以是bit,byte,packet )的抽象描述。
C++流是指信息从外部输入设备(如键盘)向计算机内部(如内存)输入和从内存向外部输出设备(显示器)输出的过程。这种输入输出的过程被形象的比喻为“流”。
它的特性是:有序连续、具有方向性
为了实现这种流动,C++定义了I/O标准类库,这些每个类都称为流/流类,用以完成某方面的功能
三、C++IO流
C++系统实现了一个庞大的类库,其中ios为基类,其他类都是直接或间接派生自ios类
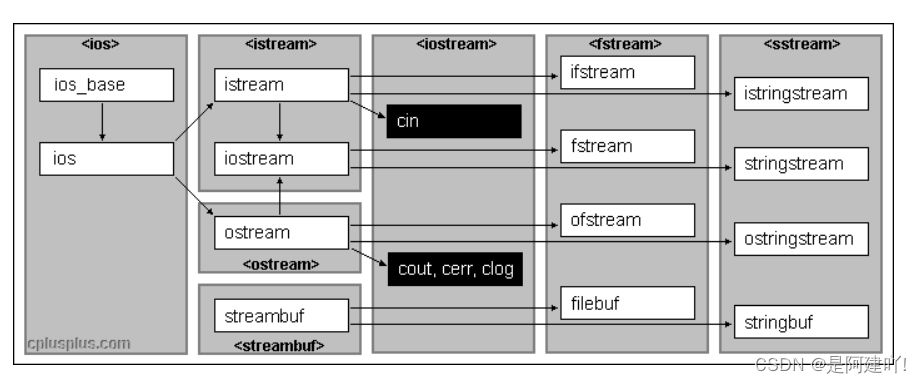
3.1 C++标准IO流
C++标准库提供了4个全局流对象cin、cout、cerr、clog,使用cout进行标准输出,即数据从内存流向控制台(显示器)。使用cin进行标准输入即数据通过键盘输入到程序中,同时C++标准库还提供了cerr用来进行标准错误的输出,以及clog进行日志的输出,从上图可以看出,cout、cerr、clog是ostream类的三个不同的对象,因此这三个对象现在基本没有区别,只是应用场景不同。
在使用时候必须要包含文件并引入std标准命名空间。
注意:
- cin为缓冲流。键盘输入的数据保存在缓冲区中,当要提取时,是从缓冲区中拿。如果一次输入过多,会留在那儿慢慢用,如果输入错了,必须在回车之前修改,如果回车键按下就无法挽回了。只有把输入缓冲区中的数据取完后,才要求输入新的数据。
- 输入的数据类型必须与要提取的数据类型一致,否则出错。出错只是在流的状态字state中对应位置位,程序继续。
- 空格和回车都可以作为数据之间的分格符,所以多个数据可以在一行输入,也可以分行输入。但如果是字符型和字符串,则空格(ASCII码为32)无法用cin输入,字符串中也不能有空格。回车符也无法读入。
- cin和cout可以直接输入和输出内置类型数据,原因:标准库已经将所有内置类型的输入和输出全部重载了:
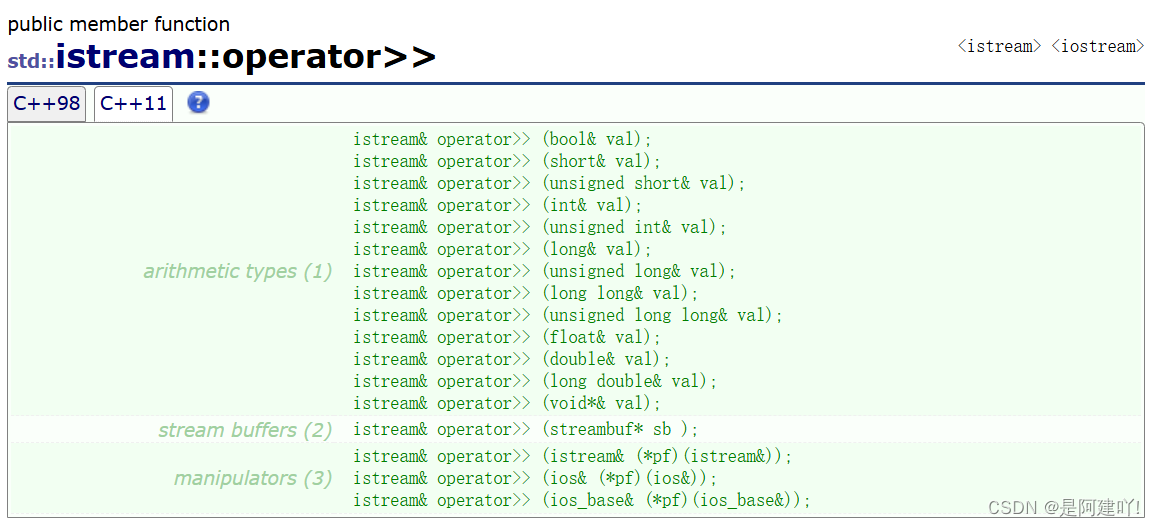
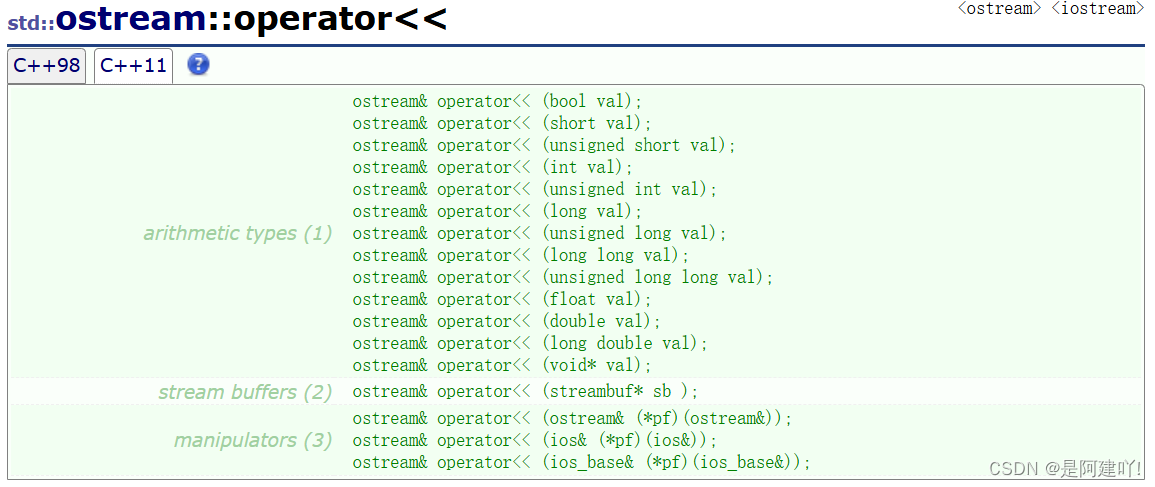
- 对于自定义类型,如果要支持cin和cout的标准输入输出,需要对<<和>>进行重载。
- 在线OJ中的输入和输出:
- 对于IO类型的算法,一般都需要循环输入:
- 输出:严格按照题目的要求进行,多一个少一个空格都不行。
- 连续输入时,vs系列编译器下在输入ctrl+Z时结束
#include- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
那么为什么这里是什么作为判断条件进行循环的呢?
以前我们学习过能作为循环判断条件的只有 bool值、整形和指针类型,而这里cin的返回值是istream并不属于他们其中的一种,那是因为什么原因呢?
原因是C++设计了一个函数 operator bool 函数,istream的对象调用了operator bool,operator bool调用时如果接收流失败,或者有结束标志,则返回false,所以这里可以做逻辑条件值。
-
istream类型对象转换为逻辑条件判断值
istream& operator>> (int& val); explicit operator bool() const;- 1
- 2
https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/ios/ios/operator_bool/
下面写一个Date类,并且在类中实现operator bool,如果Date类成员作为判断条件,那么Date类成员会调用operator boo l转换为 bool。
class Date
{
public:
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& date);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& date);
public:
Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1 , int day = 1)
:_year(year)
,_month(month)
,_day(day)
{}
Date(const Date& date)
{
if (this != &date)
{
_year = date._year;
_month = date._month;
_day = date._day;
}
}
// 这里认为year<2000作为循环判断失败条件
operator bool()
{
if (_year < 2000)
return false;
else
return true;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& date)
{
in >> date._year >> date._month >> date._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& date)
{
out << date._year << " " << date._month << " " << date._day << endl;
return out;
}
int main()
{
Date date;
// 由于Date类中定义了operator bool
// 那么作为循环判断条件时,date可以调用operator bool转换为bool
while (date)
{
cin >> date;
cout << date;
}
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
既然上面提到了类对象可以通过operator bool函数将类对象转化为bool类型,那么下面整体讲一下类型转换。
类型转换:
-
内置类型之间,相近类型可以相互转换
int main() { int i = 520; double d = 13.14; cout << "i:" << i << " d:" << d << endl; i = d; cout << "i:" << i << " d:" << d << endl; d = i; cout << "i:" << i << " d:" << d << endl; return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
-
构造函数,若有其他类型想转换为当前自定义类型可以通过构造函数实现。
自定义类型 <-- 内置类型自定义类型 <-- 自定义类型class A { public: A(int i) { // ... } }; class B { public: B(const A& a) { // ... } }; int main() { // 自定义类型 <-- 内置类型 int i = 520; A a = 1; string s = "I Love Y"; // 自定义类型 <-- 自定义类型 B b = b; string ss; string::const_iterator it = ss.begin(); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
-
operator type() 可以实现
内置类型 <-- 自定义类型class Convert { public: operator int() { // ... return 520; } }; int main() { // 内置类型 <-- 自定义类型 Convert con; int i = con; return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
3.2 C++文件IO流
C++根据文件内容的数据格式分为二进制文件和文本文件。采用文件流对象操作文件的一般步骤:
- 定义一个文件流对象
ifstream ifile(只输入用)
ofstream ofile(只输出用)
fstream iofile(既输入又输出用) - 使用文件流对象的成员函数打开一个磁盘文件,使得文件流对象和磁盘文件之间建立联系
- 使用提取和插入运算符对文件进行读写操作,或使用成员函数进行读写
- 关闭文件
3.2.1 二进制读写
class Date
{
public:
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& date);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& date);
public:
Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1 , int day = 1)
:_year(year)
,_month(month)
,_day(day)
{}
Date(const Date& date)
{
if (this != &date)
{
_year = date._year;
_month = date._month;
_day = date._day;
}
}
// 这里认为year<2000作为循环判断失败条件
operator bool()
{
if (_year < 2000)
return false;
else
return true;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& date)
{
in >> date._year >> date._month >> date._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& date)
{
out << date._year << " " << date._month << " " << date._day << endl;
return out;
}
struct ServerInfo
{
char _address[32];
double _x;
Date _date;
};
// 二进制读写
class BinIO
{
public:
BinIO(const char* filename = "info.txt")
:_filename(filename)
{}
void Write(const ServerInfo& winfo)
{
ofstream ofs(_filename, ofstream::out | ofstream::binary);
ofs.write((char*)&winfo,sizeof(winfo));
}
void Read(ServerInfo& rinfo)
{
ifstream ifs(_filename, ifstream::in | ifstream::binary);
ifs.read((char*)&rinfo, sizeof(rinfo));
}
private:
string _filename;
};
// 写
int main()
{
ServerInfo sinfo = { "192.128.64.32", 3.14, { 1949,10,1 } };
BinIO BIO;
BIO.Write(sinfo);
return 0;
}
读
//int main()
//{
// ServerInfo sinfo;
//
// BinIO BIO;
//
// BIO.Read(sinfo);
//
// return 0;
//}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
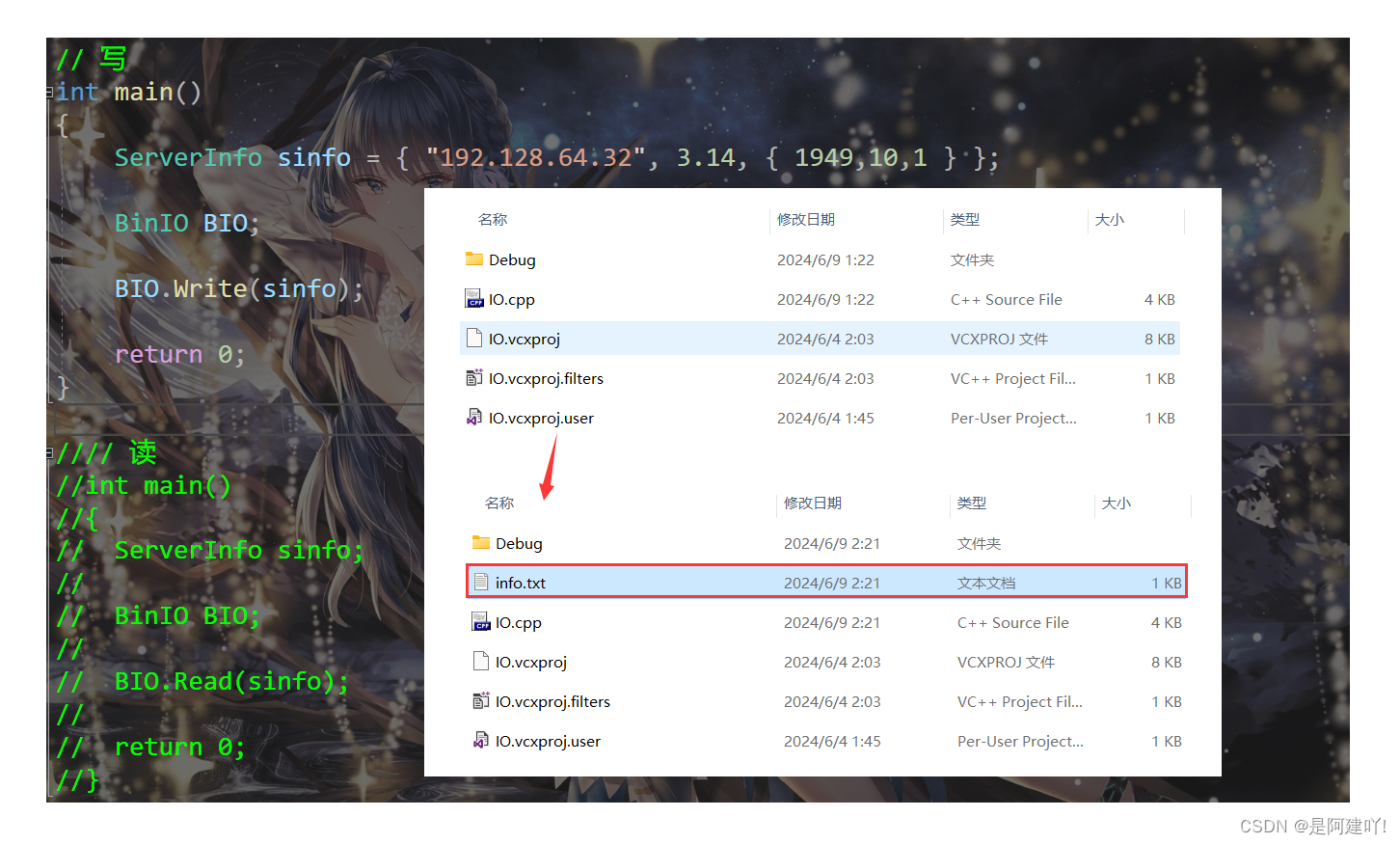
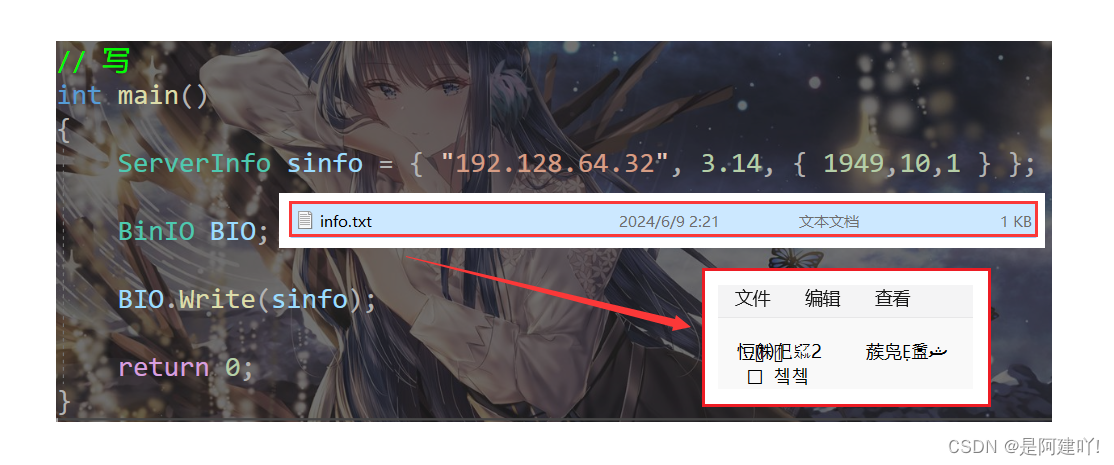
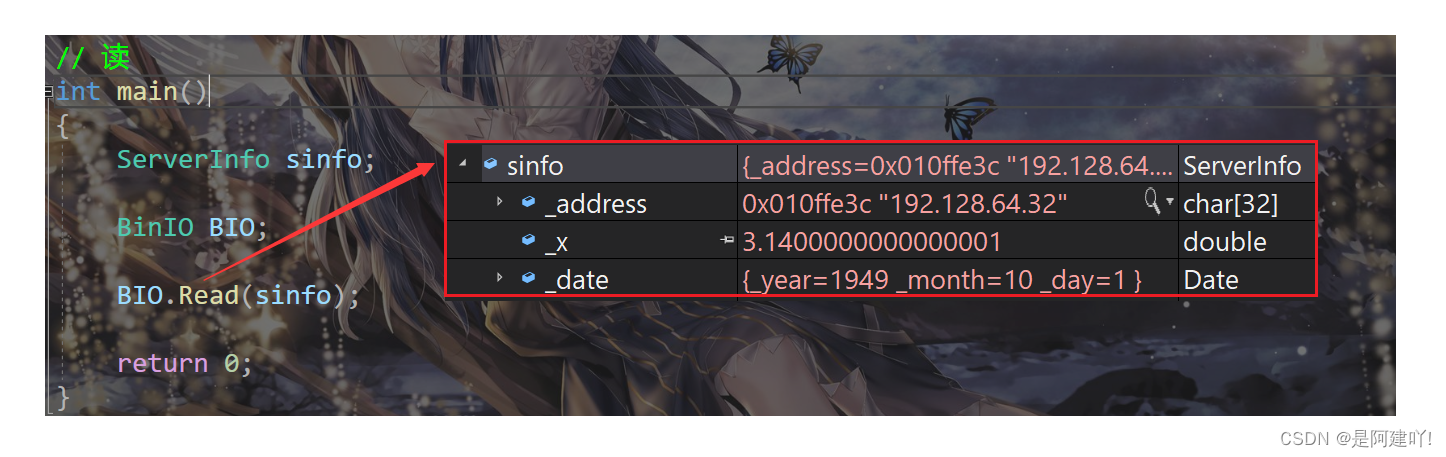
这里提一个很多初学者可能犯的错误,那就是在结构体 ServerInfo 中,不使用char* 而使用string,会出现什么问题呢?我们使用代码展示一下。
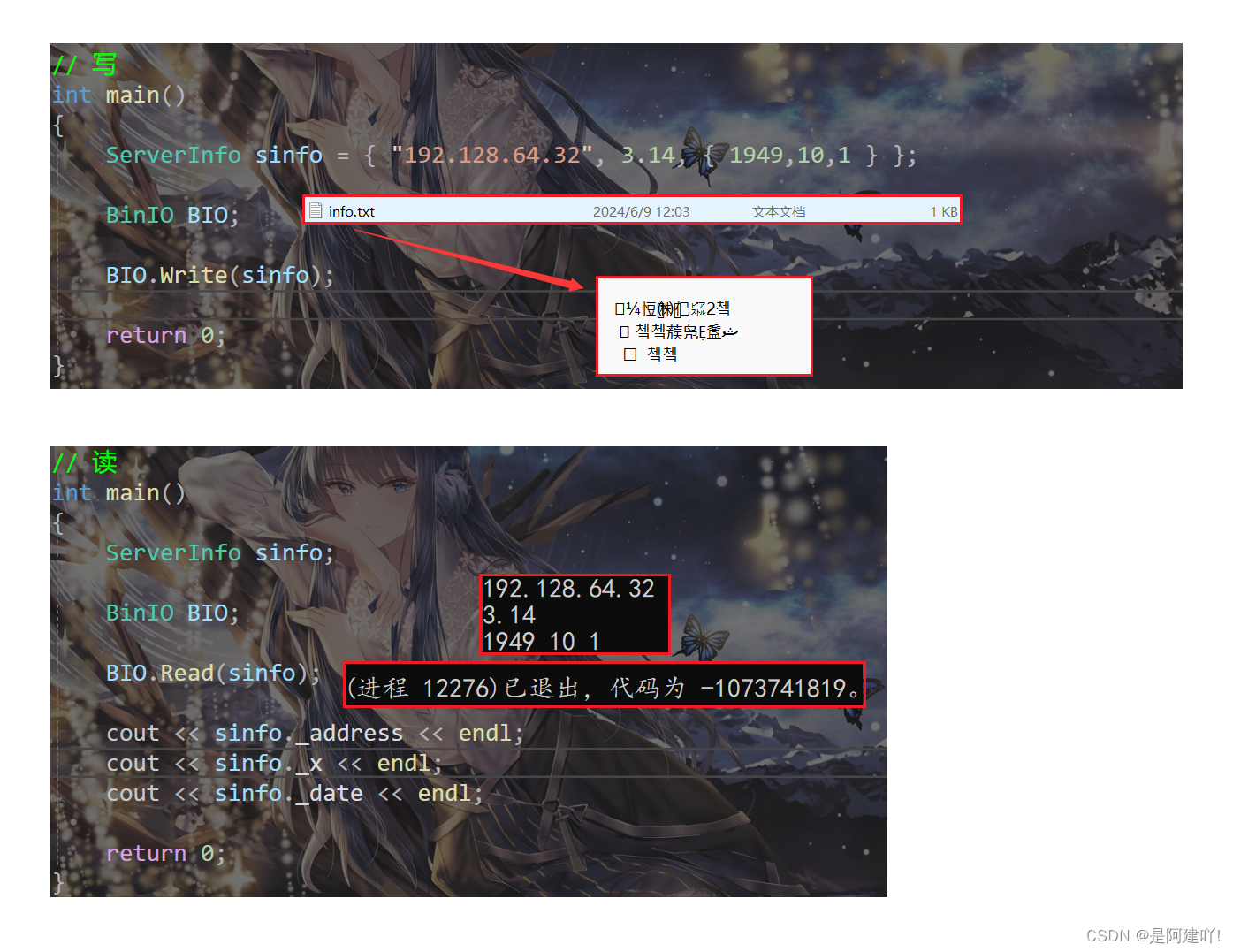
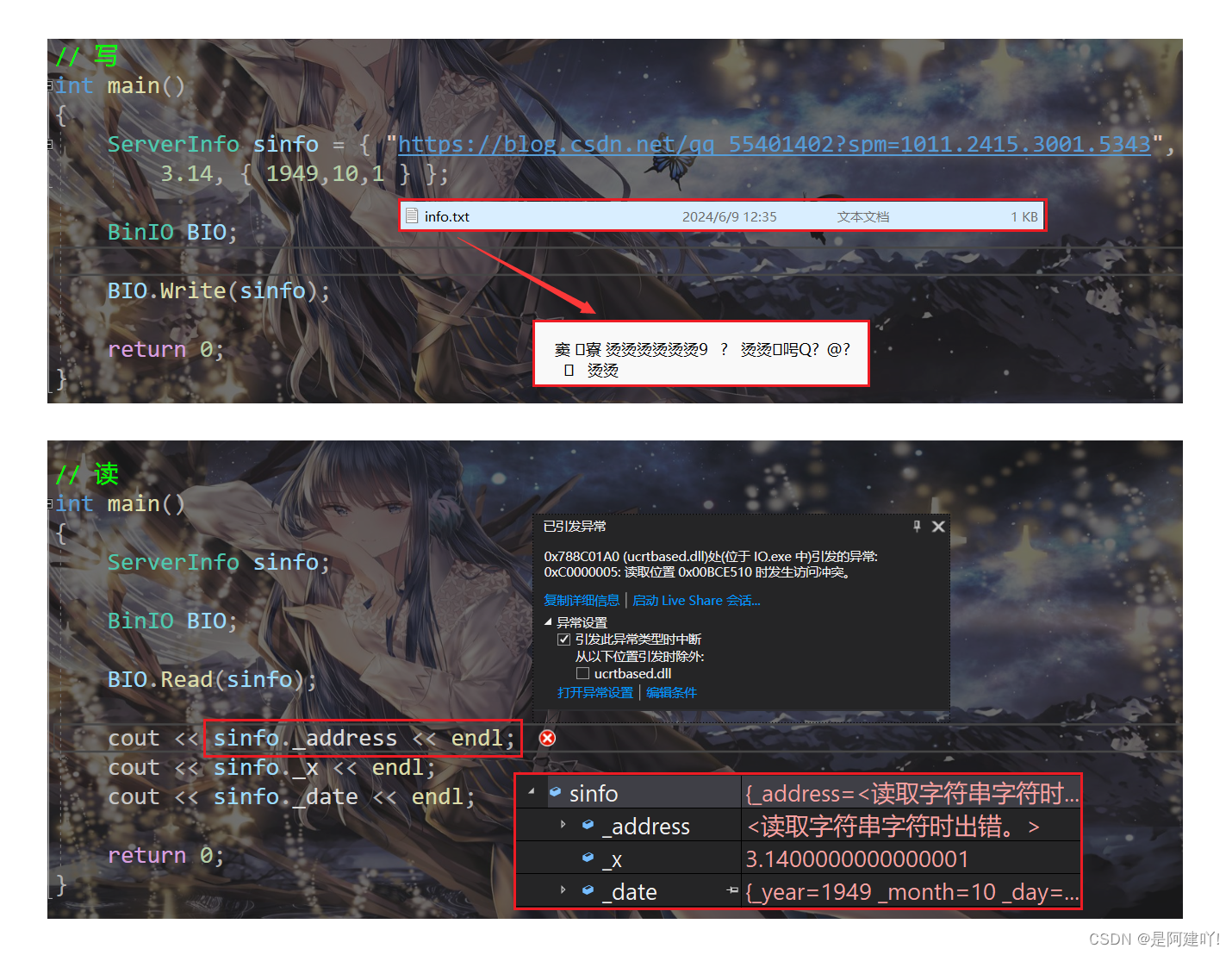
我们会发现写入文件时没有问题,但是读入内存中访问时程序崩溃了,其他的都读进去了,只有string读入有问题,为什么呢?从string的底层和操作系统的内存管理入手,string是如何存字符串的呢?
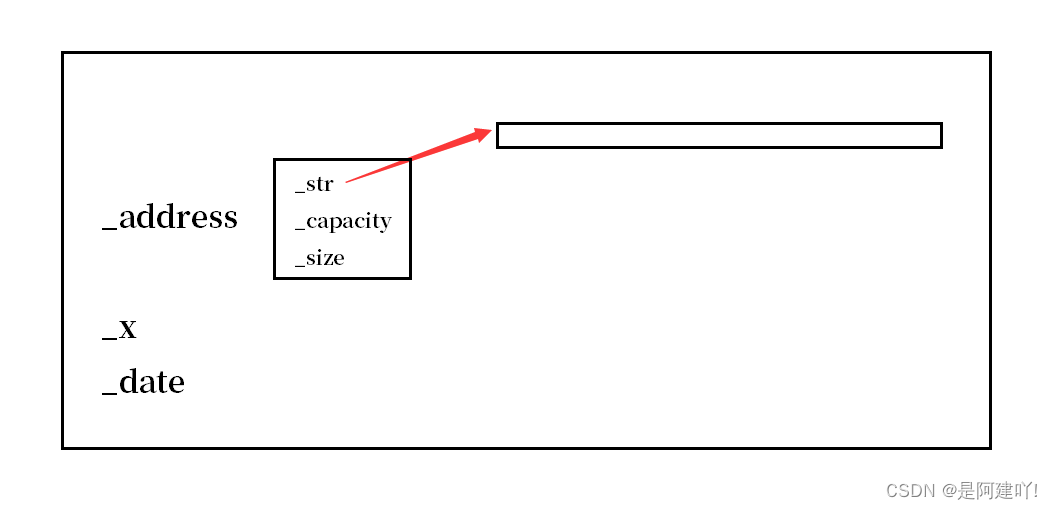
string中存储的_str,_capacity和_size,当把string以二进制的方式写进文件时,是将_str,_capacity和_size写入文件,而并未将string存储的字符串写入文件,那么以二进制读的方式读进内存中时,也是直接将_str,_capacity和_size读进内存,而写和读是两个进程,当写结束时,string中_str指向的内容会被销毁,当读时会将原来的_str读进来,而原来的空间已经被销毁了,那么这里的_str就是野指针,访问就会使程序崩溃。
上面是将读和写分为两个进程,那么将读和写写入一个进程会怎么样呢?
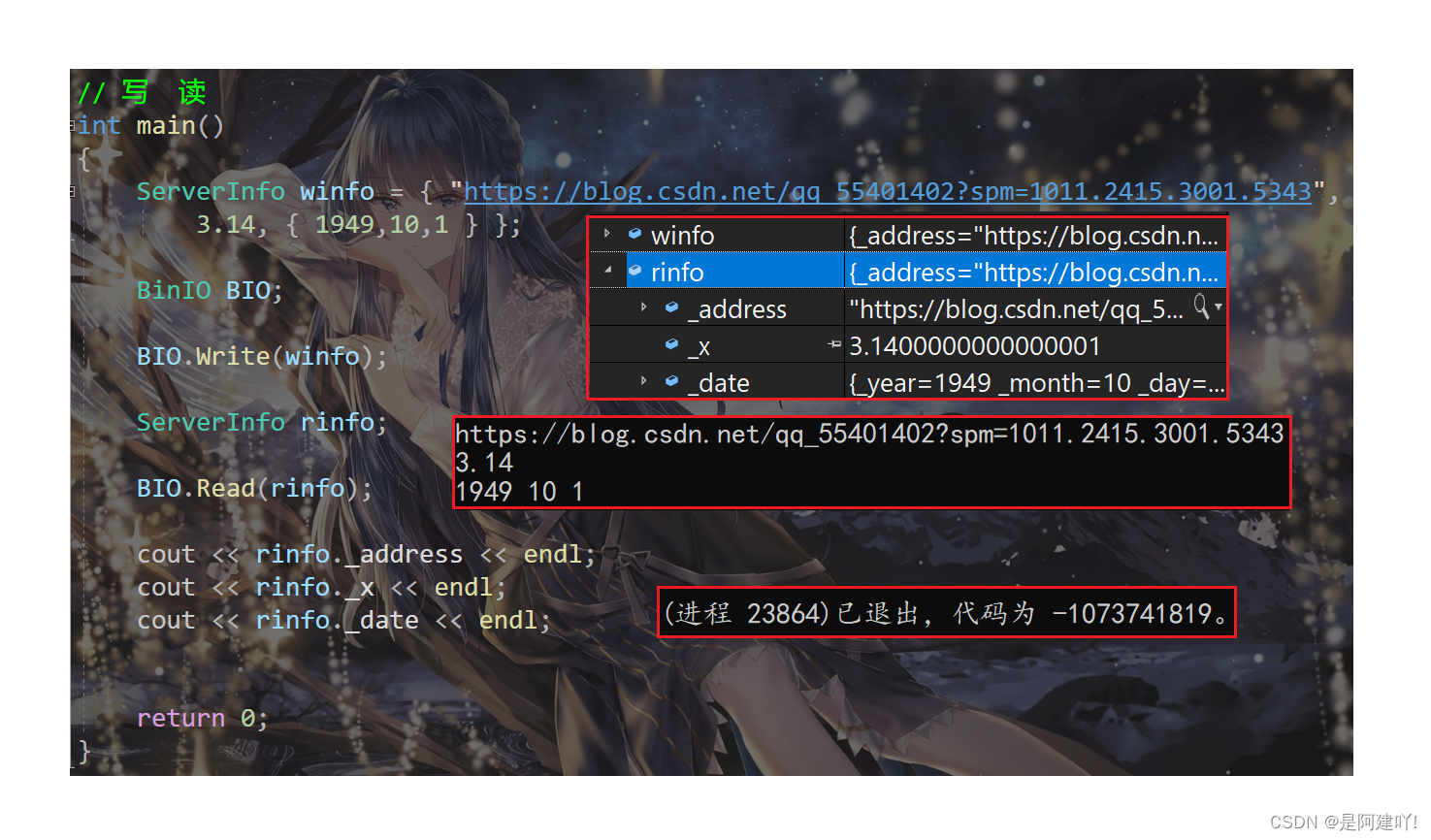
通过上面的图片可以发现,string的读写没什么问题,但是程序还是崩溃了,为什么呢?因为这里存在string浅拷贝的问题,析构时析构了两次导致了程序的崩溃。但是我们一般在使用的时候,读写不会在同一个进程。
在使用二进制读写时,不要使用容器,如果要使用容器就要使用下面的文本读写。
二进制读写有一个很大的问题,就是写进去的内容看不见可能是乱码。
3.2.2 文本读写
文本读写与二进制读写相比的难在将所有需要写入的数据转换为字节流,字节流可以通过字符串转换而来,那么这里的问题可以转化为将所有需要写入的数据转换为字符串。还是以结构体 ServerInfo 举例,ServerInfo中的string类型的数据可以使用c_str直接取到字符串,ServerInfo中的double类型的数据可以使用to_string转换为字符串,那么ServerInfo中的Date类型怎么处理呢?我们可以自己设计一个函数,将Date类型中的数据全部使用to_string转换为字符串再组合返回。
但是C++中有更为方便的方法,那就是使用ostream对象调用operator<<函数将数据写入到文件中,而这里的operator<<只有参数为内置类型时才能使用,如果有自定义类型应该怎么办呢?我们可以在自定义类型的类中重载一个operator<<,那么在写自定义类型数据时就可以调用它的operator<<将数据写入文件中了。同理,如果想要将文件中的内容读出来,就使用operator>>函数将数据读出,若有自定义类型,在自定义类型的类中重载一个operator<<函数。
顺便提一下,如果在纯C语言的情况下,也需要将数据转换为字节流,也可以说是转换为字符串,C语言中int类型可以使用itoa函数将int类型转换为字符串,那么如果是double类型呢?可能会有人想不到如何转换为double,其实很简单,C语言中有这么一个函数sprintf函数,可以将任意内置类型的数据转化为字符串,相比于itoa函数,使用sprintf函数会更好用一些。
class Date
{
public:
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& date);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& date);
public:
Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
Date(const Date& date)
{
if (this != &date)
{
_year = date._year;
_month = date._month;
_day = date._day;
}
}
// 这里认为year<2000作为循环判断失败条件
operator bool()
{
if (_year < 2000)
return false;
else
return true;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& date)
{
in >> date._year >> date._month >> date._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& date)
{
out << date._year << " " << date._month << " " << date._day << endl;
return out;
}
struct ServerInfo
{
string _address;
double _x;
Date _date;
};
// 文本读写
class TestIO
{
public:
TestIO(const char* filename = "info2.txt")
:_filename(filename)
{}
void Write(const ServerInfo& winfo)
{
// 覆盖写
ofstream ofs(_filename);
ofs << winfo._address << endl;
ofs << winfo._x << endl;
ofs << winfo._date << endl;
}
void Read(ServerInfo& rinfo)
{
ifstream ifs(_filename);
ifs >> rinfo._address;
ifs >> rinfo._x;
ifs >> rinfo._date;
}
private:
string _filename;
};
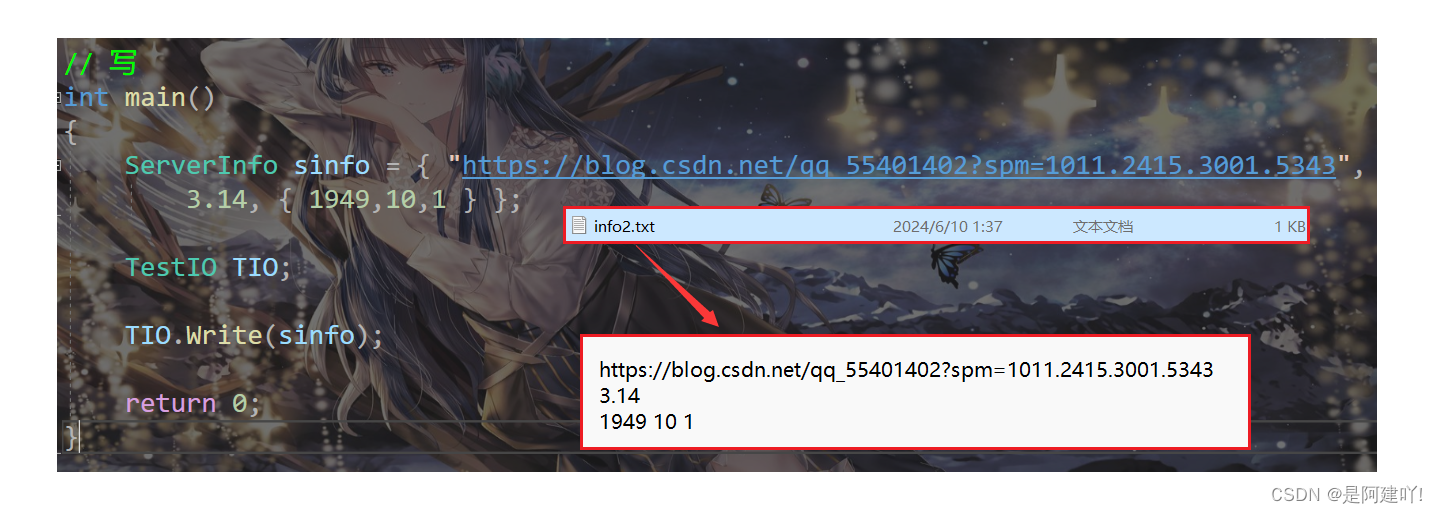
写
//int main()
//{
// ServerInfo sinfo = { "https://blog.csdn.net/qq_55401402?spm=1011.2415.3001.5343",
// 3.14, { 1949,10,1 } };
//
// TestIO TIO;
//
// TIO.Write(sinfo);
//
// return 0;
//}
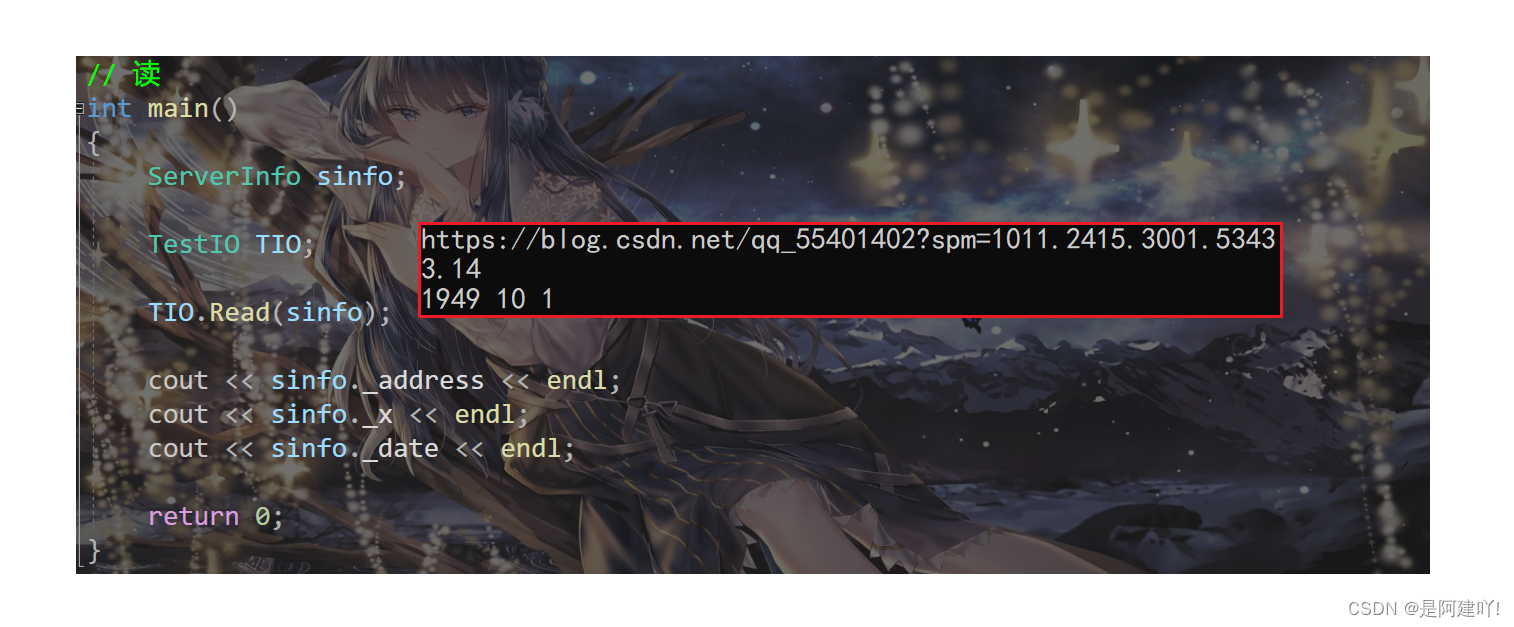
// 读
int main()
{
ServerInfo sinfo;
TestIO TIO;
TIO.Read(sinfo);
cout << sinfo._address << endl;
cout << sinfo._x << endl;
cout << sinfo._date << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
四、stringstream的简单介绍
在C语言中,如果想要将一个整形变量的数据转化为字符串格式,如何去做?
- 使用itoa()函数
- 使用sprintf()函数
但是两个函数在转化时,都得需要先给出保存结果的空间,那空间要给多大呢,就不太好界定,而且转化格式不匹配时,可能还会得到错误的结果甚至程序崩溃。
在C++中,可以使用stringstream类对象来避开此问题。
在程序中如果想要使用stringstream,必须要包含头文件。在该头文件下,标准库三个类:istringstream、ostringstream 和 stringstream,分别用来进行流的输入、输出和输入输出操作,本文主要介绍stringstream。
stringstream主要可以用来:
- 将数值类型数据格式化为字符串
#include- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 字符串拼接
int main()
{
stringstream sstream;
// 将多个字符串放入 sstream 中
sstream << "first" << " " << "string,";
sstream << " second string";
cout << "strResult is: " << sstream.str() << endl;
// 清空 sstream
sstream.str("");
sstream << "third string";
cout << "After clear, strResult is: " << sstream.str() << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 序列化和反序列化结构数据
序列化:将各种信息转换成字符串
反序列化:将字符串中的信息提取出来转换为内存数据
#include- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
注意:
- stringstream实际是在其底层维护了一个string类型的对象用来保存结果。
- 多次数据类型转化时,一定要用clear()来清空,才能正确转化,但clear()不会将stringstream底层的string对象清空。
- 可以使用s. str(“”)方法将底层string对象设置为""空字符串。
- 可以使用s.str()将让stringstream返回其底层的string对象。
- stringstream使用string类对象代替字符数组,可以避免缓冲区溢出的危险,而且其会对参数类型进行推演,不需要格式化控制,也不会出现格式化失败的风险,因此使用更方便,更安全。
结尾
如果有什么建议和疑问,或是有什么错误,大家可以在评论区中提出。
希望大家以后也能和我一起进步!!??
如果这篇文章对你有用的话,希望大家给一个三连支持一下!!??


评论记录:
回复评论: